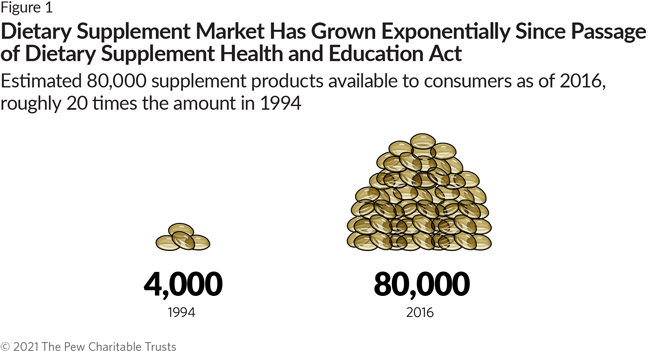
The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) plays a crucial role in regulating supplements. This act, passed in 1994, impacts how dietary supplements are marketed and sold.
Understanding the pros and cons of DSHEA is important for consumers and industry professionals alike. The act allows for a broader range of supplements to be available without strict FDA approval. This means more options for consumers. But it also raises concerns about safety and efficacy.
Some praise DSHEA for promoting health freedom. Others worry about the potential risks. In this blog post, we will explore both sides of the argument. This will help you understand the benefits and drawbacks of DSHEA. Stay tuned to make informed decisions about your health and supplement choices.
Credit: www.pewtrusts.org
Introduction To Dshea
The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) is a crucial law. It governs dietary supplements in the United States. This act was passed in 1994. It aims to ensure the safety and quality of supplements. It also provides guidelines for their manufacturing and labeling.
Background And Purpose
The DSHEA was created in response to the growing supplement market. By the early 1990s, many people were using supplements. There was a need to regulate this industry. The primary purpose of DSHEA is to protect consumers. It ensures that supplements are safe and properly labeled. This law also supports the dietary supplement industry. It allows for the continued sale of these products without undue restrictions.
| Objective | Description |
|---|---|
| Consumer Safety | Ensure supplements are safe to consume |
| Proper Labeling | Provide accurate information on packaging |
| Industry Support | Allow supplements to be sold freely |
Legislative History
The DSHEA was passed in 1994. It was a response to public demand. People wanted access to dietary supplements. Before DSHEA, the FDA had strict control over supplements. Many products were removed from the market.
DSHEA changed this. It redefined supplements as a category separate from drugs. This allowed for more lenient regulations. The law was supported by many lawmakers. They believed in the benefits of dietary supplements.
- Passed in 1994
- Response to public demand
- Redefined supplements
- Supported by lawmakers
Key Provisions Of Dshea
The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) was passed in 1994. It provides a regulatory framework for dietary supplements in the United States. Understanding its key provisions is vital. It helps consumers make informed choices. It also guides manufacturers in compliance. This section covers the main provisions of DSHEA.
Definition Of Dietary Supplements
DSHEA defines what constitutes a dietary supplement. According to the act, a dietary supplement is:
- A product taken by mouth
- Contains dietary ingredients like vitamins, minerals, herbs, or amino acids
- Meant to supplement the diet
Dietary supplements come in various forms. This includes tablets, capsules, powders, and liquids. The act ensures that products are labeled as dietary supplements. This helps consumers identify them easily.
Regulatory Framework
DSHEA establishes a regulatory framework for dietary supplements. It gives the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversight responsibilities. The key regulatory aspects are:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) | Manufacturers must follow GMPs. This ensures product quality and safety. |
| Labeling Requirements | Products must have clear and accurate labels. Labels should list all ingredients. |
| Safety Monitoring | FDA monitors the safety of dietary supplements. They can take action if products are found unsafe. |
| Claims and Advertising | Manufacturers can make health claims. These claims must be truthful and not misleading. |
DSHEA also distinguishes dietary supplements from drugs. Supplements do not require pre-market approval by the FDA. But manufacturers must ensure their products are safe. They must also ensure their claims are backed by evidence.
Overall, DSHEA aims to balance consumer access to dietary supplements with safety and quality standards. It empowers both consumers and regulators. Understanding these provisions helps in making informed choices about dietary supplements.
Benefits Of Dshea
The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) provides several benefits. It has changed the landscape of dietary supplements in the US. Let’s delve into the key advantages it brings.
Consumer Access To Supplements
DSHEA ensures consumers have easier access to dietary supplements. This law allows supplements to be marketed without FDA approval. Hence, people can find a wide range of products.
Consumers can choose from vitamins, minerals, herbs, and amino acids. They can select supplements based on their needs and preferences. This access empowers individuals to take charge of their health. They can use supplements to support their well-being.
Innovation In The Supplement Industry
DSHEA fosters innovation in the supplement industry. Companies are encouraged to create new and improved products. The law allows manufacturers to introduce unique supplements faster.
Here are some ways DSHEA promotes innovation:
- Reduced regulatory barriers
- Increased market opportunities
- Enhanced research and development efforts
Manufacturers can experiment with new ingredients and formulations. They can address specific health concerns with innovative products. This leads to a dynamic and evolving supplement market. Consumers benefit from cutting-edge options.
DSHEA plays a crucial role in shaping the supplement industry. It ensures consumer access and encourages innovation. These benefits have a significant impact on the market and public health.
Consumer Protection Under Dshea
The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) plays a crucial role in consumer protection. It establishes guidelines ensuring the safety and quality of dietary supplements in the market. This act aims to safeguard consumers while also providing them with accurate information.
Labeling Requirements
Under DSHEA, dietary supplements must adhere to strict labeling requirements. Labels must include:
- The name of the product
- The amount of the dietary ingredient
- A complete list of ingredients
- The name and address of the manufacturer
This ensures consumers have access to clear and accurate information about what they are consuming.
Good Manufacturing Practices
DSHEA enforces Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) to ensure the quality of dietary supplements. GMPs include:
- Proper design and control of manufacturing processes
- Maintenance of clean and hygienic manufacturing facilities
- Accurate and complete record-keeping
- Regular testing for contaminants and ingredient potency
These practices help maintain the integrity and safety of dietary supplements, protecting consumers from potential harm.
Criticisms Of Dshea
The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) has been a topic of debate since its enactment. While it offers benefits, it also has its criticisms. Let’s explore some of the major concerns raised against DSHEA.
Lack Of Pre-market Testing
One major criticism is the lack of pre-market testing. Unlike prescription drugs, dietary supplements do not need to be tested for safety before they are sold. This means that potentially harmful products can reach consumers.
Consumers often assume that supplements are safe. This assumption can lead to serious health risks. The absence of mandatory safety testing can result in products with hidden dangers.
The FDA’s role under DSHEA is limited. They can only act after a product is proven harmful. This reactive approach is seen as insufficient for protecting public health.
Misleading Health Claims
Another significant issue is the presence of misleading health claims. Under DSHEA, manufacturers can make broad claims about their products without rigorous proof. This can mislead consumers into believing in unverified benefits.
For instance, many supplements claim to boost immunity or cure ailments. Such claims can be persuasive but lack scientific backing. Consumers may spend money on ineffective or even harmful products.
Regulation of advertising is also weak. This allows companies to market their products aggressively. Consumers are left to discern the truth from exaggerated claims.
In summary, the criticisms of DSHEA center around safety and honesty. Without pre-market testing and stricter claim regulations, consumers face risks. Awareness of these issues is crucial for making informed decisions.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Impact On Public Health
The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) has had a significant impact on public health. This act, passed in 1994, regulates dietary supplements in the United States. It aims to ensure that these products are safe and properly labeled. While the act has made supplements more accessible, it has also raised some public health concerns.
Safety Concerns
One of the major safety concerns under DSHEA is the regulation standards. Unlike prescription drugs, dietary supplements do not require FDA approval before they are marketed. This means that some supplements may contain unsafe ingredients. Quality control can also vary significantly between products.
Consumers may not always know what they are getting. This lack of strict regulation can lead to health risks, especially for people with underlying health conditions. It is important to research and choose supplements from reputable sources.
Adverse Event Reporting
Adverse event reporting is another critical aspect of DSHEA. Under this act, manufacturers must report serious adverse events to the FDA. However, minor adverse events do not need to be reported. This can lead to an incomplete picture of the supplement’s safety profile.
| Event Type | Reporting Requirement |
|---|---|
| Serious Adverse Events | Must be reported to the FDA |
| Minor Adverse Events | Not required to be reported |
This reporting system helps monitor safety but has limitations. Consumers must also report any adverse effects they experience. This can help improve the safety and efficacy of dietary supplements.
Economic Implications
The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) has significant economic implications. Understanding these implications helps stakeholders make informed decisions. This section explores the economic aspects of DSHEA, including market growth and regulatory costs.
Market Growth
DSHEA has spurred remarkable growth in the dietary supplement market. The act allows supplements to reach consumers without stringent FDA approval. This ease of entry has encouraged new businesses to emerge.
The dietary supplement market is now worth billions of dollars. Many companies benefit from the growing demand for health products. Consumers have more options, leading to increased sales and competition.
A growing market creates jobs and boosts the economy. More businesses mean more employment opportunities. This growth positively impacts local and global economies.
Regulatory Costs
Regulating dietary supplements incurs significant costs. DSHEA requires companies to ensure product safety and labeling accuracy. These regulations impose financial burdens on businesses.
Small businesses may struggle with these costs. They often lack the resources to comply with all regulations. This can limit their market entry and growth potential.
However, regulatory costs also protect consumers. Ensuring product safety and accurate labeling builds trust. This trust can lead to increased sales and a stronger market presence.
| Economic Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Market Growth | Increased sales, job creation, and competition |
| Regulatory Costs | Financial burden on businesses, especially small ones; consumer protection |
In summary, DSHEA has both positive and negative economic implications. Market growth benefits the economy, but regulatory costs can be a challenge. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses and consumers.
Future Of Dietary Supplement Regulation
The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994 has shaped how dietary supplements are regulated in the U.S. But the landscape is changing. As new challenges emerge, there is a growing conversation about the future of dietary supplement regulation. This section explores proposed reforms and global regulatory trends.
Proposed Reforms
Many experts believe the current regulations need updates. They argue for stronger safety standards and more transparency. Here are some of the proposed reforms:
- Pre-market approval: Requiring supplements to be tested before they hit the market.
- Label accuracy: Ensuring labels accurately reflect ingredients and dosages.
- Adverse event reporting: Mandating companies to report side effects promptly.
Global Regulatory Trends
Looking at other countries can provide insight. Many nations have stricter rules than the U.S. Here are some global regulatory trends:
- European Union: Supplements must meet strict safety and labeling requirements.
- Australia: Supplements are classified as medicines and require approval.
- Japan: Functional foods category with rigorous standards for health claims.
A table comparing different regulatory approaches can highlight the differences:
| Region | Regulatory Approach |
|---|---|
| United States | Less stringent, post-market regulation |
| European Union | Strict pre-market safety and labeling requirements |
| Australia | Supplements classified as medicines, require approval |
| Japan | Functional foods with rigorous standards for health claims |
The future of dietary supplement regulation is evolving. The balance between safety and accessibility will shape the industry.

Credit: info.davincilabs.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Dietary Supplement Health And Education Act?
The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) was enacted in 1994. It regulates dietary supplements. It ensures safety and accurate labeling. It allows consumers to access a wide range of supplements.
What Are The Benefits Of Dshea?
DSHEA provides consumer access to a variety of supplements. It ensures product safety and accurate labeling. It also promotes research and innovation in the supplement industry.
What Are The Drawbacks Of Dshea?
DSHEA has limited regulation and oversight of supplement manufacturers. It may lead to potential safety risks. It can result in misleading claims on product labels.
How Does Dshea Impact Consumers?
DSHEA allows consumers to access various supplements. It ensures safety and accurate labeling. However, it also requires consumers to be cautious about product claims.
Conclusion
Navigating the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act has its challenges. Benefits include access to diverse supplements. Yet, regulation gaps can pose risks. Consumers need to stay informed. Choosing reputable brands helps ensure safety. Weigh pros and cons before making decisions.
Always consult health professionals. Awareness is key to safe supplement use.

“As the voice behind Radiant Glow Health, we are dedicated to being your ultimate wellness and vitality companion. Our mission is to inspire and guide you on your journey to a healthier and more vibrant life. Join us as we explore holistic health practices and empower you to radiate wellness from within.”



