Understanding health inequalities is crucial. It affects everyone’s well-being and life quality.
Health inequalities refer to differences in health status or distribution of health resources. These differences arise from social, economic, and environmental factors. Recognizing the reasons behind health inequalities helps address these gaps. It also ensures fair access to healthcare for all.
Knowledge in this area allows policymakers to create better health strategies. This, in turn, improves public health outcomes. By understanding these reasons, we can work towards a healthier, more equitable society. This awareness fosters empathy and drives action, making health equity a shared goal. Join us as we explore why grasping these underlying reasons is essential.
Roots Of Health Inequalities
Understanding the reasons underlying health inequalities is crucial for creating a fair and just society. Health inequalities arise from various factors, often deeply rooted in economic and social structures. These inequalities not only impact individuals but also strain public health systems and affect overall societal well-being. By exploring the roots of health inequalities, we can better address these issues and work towards health equity for all.
Economic Factors
Economic factors play a significant role in health inequalities. One’s socioeconomic status often determines their access to healthcare and overall health outcomes. Individuals with higher incomes typically have better access to quality healthcare services, including preventative care. This advantage allows them to manage and prevent health issues more effectively.
In contrast, those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds often face financial barriers that limit their access to essential healthcare services. This lack of access can lead to poorer health outcomes and exacerbate existing health disparities. Here are some key economic factors influencing health inequalities:
- Income Level: Higher income levels generally correlate with better health outcomes.
- Employment Status: Unemployed individuals may lack health insurance and access to healthcare.
- Housing Quality: Poor living conditions can contribute to health problems.
- Nutrition: Limited financial resources can restrict access to healthy food options.
Addressing these economic factors is vital for achieving health equity. Policies that support affordable healthcare, living wages, and access to nutritious food can help reduce health disparities. Investing in marginalized communities and providing economic opportunities can improve public health and promote social justice.
Social Determinants
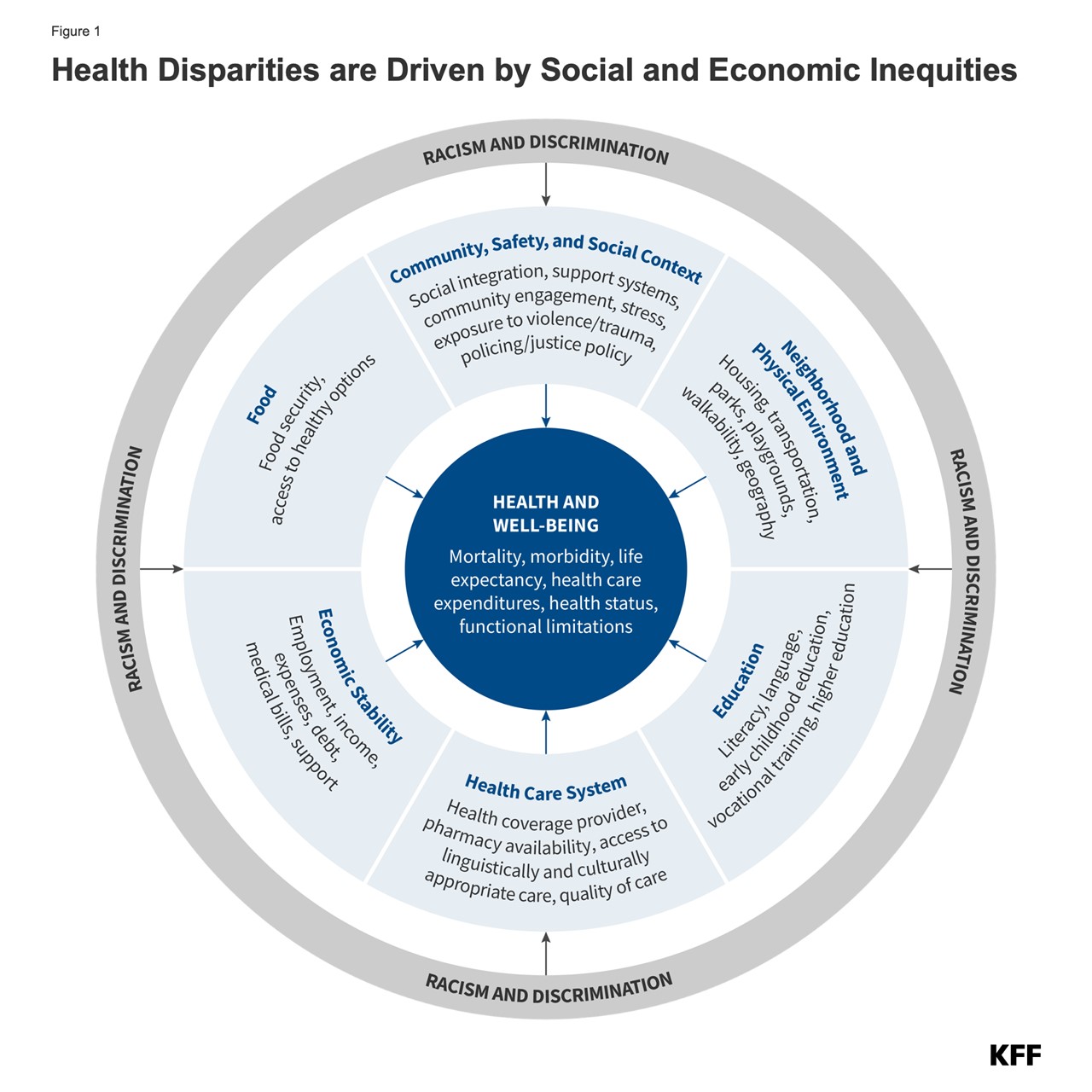
Social determinants of health are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age. These determinants have a profound impact on health outcomes and contribute significantly to health inequalities. Systemic inequalities in education, employment, and social support networks can create barriers to good health.
Some key social determinants include:
- Education: Higher educational attainment is linked to better health literacy and healthier lifestyles.
- Social Support: Strong social networks can provide emotional and practical support, improving health outcomes.
- Discrimination: Marginalized communities often face systemic discrimination, affecting their access to healthcare and other resources.
- Neighborhood and Physical Environment: Safe neighborhoods with access to parks and recreational facilities promote physical activity and well-being.
Improving these social determinants requires a comprehensive approach that addresses systemic inequalities. Public health initiatives should focus on creating supportive environments, enhancing educational opportunities, and promoting social justice. By tackling these root causes, we can work towards a society where everyone has the opportunity to achieve optimal health.
Credit: www.kff.org
Impact On Communities
Understanding the reasons underlying health inequalities is crucial. This knowledge can transform communities. Health inequalities affect everyone. They can shape the well-being of entire neighborhoods. By addressing these disparities, we can create healthier, stronger communities.
Health Outcomes
Health inequalities significantly impact health outcomes. These disparities can lead to higher rates of illness and disease in certain groups. For instance, low-income communities often face barriers to accessing healthcare. This can result in untreated conditions and worse health outcomes.
Key factors affecting health outcomes include:
- Access to healthcare services
- Quality of available healthcare
- Economic stability
- Education levels
- Environmental conditions
Access to healthcare services is a major factor. Communities with limited access often experience higher rates of chronic diseases. These include diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory conditions. Quality of available healthcare also plays a role. In areas with fewer healthcare resources, individuals may receive inadequate care.
Economic stability influences health outcomes too. People in stable financial situations can afford healthier lifestyles. They can buy nutritious foods and live in safer environments. Education levels correlate with health outcomes as well. Higher education often leads to better job opportunities and healthier living conditions.
Environmental conditions, such as air quality and housing, also impact health. Poor air quality can lead to respiratory issues. Inadequate housing can cause stress and physical health problems. Thus, understanding these factors is essential for improving health outcomes.
Social Cohesion
Health inequalities also affect social cohesion. Communities with high levels of inequality often experience social fragmentation. This can weaken community bonds and reduce trust among residents.
Key aspects of social cohesion include:
- Trust among community members
- Community participation
- Sense of belonging
- Mutual support
Trust among community members is vital. High levels of health inequality can reduce trust. People may feel alienated or marginalized. This can lead to social isolation and a lack of community spirit.
Community participation is another crucial factor. When people feel excluded due to health disparities, they may withdraw from community activities. This reduces opportunities for social interaction and support.
A sense of belonging is essential for social cohesion. Health inequalities can make individuals feel disconnected from their community. They may believe their needs are not being met or valued.
Mutual support strengthens communities. In areas with high health inequality, mutual support may decline. People struggling with health issues may have less capacity to help others. This can lead to a cycle of reduced support and increased inequality.
By understanding the reasons underlying health inequalities, we can work to improve social cohesion. Stronger community bonds lead to better overall health and well-being.
Policy Implications
Understanding the reasons underlying health inequalities is crucial for creating effective public health policies. These policies can address the root causes of disparities and promote equity in healthcare. By understanding the factors that contribute to health inequalities, policymakers can create targeted interventions. These interventions can improve health outcomes for disadvantaged communities. In this section, we will discuss the policy implications of understanding health inequalities, focusing on resource allocation and legislative changes.
Resource Allocation
Resource allocation plays a vital role in addressing health disparities. Policymakers need to ensure that resources are distributed equitably. This can improve access to healthcare for underserved communities. Effective resource allocation can help address systemic inequality and promote community health.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Funding for Health Education: Investing in health education can empower individuals to make informed health decisions.
- Infrastructure Development: Building healthcare facilities in underserved areas can improve access to healthcare.
- Support for Community Health Programs: Community health programs can address specific health needs of local populations.
Effective resource allocation requires an understanding of the social determinants of health. These determinants include socioeconomic factors such as income, education, and employment. By addressing these factors, policymakers can create a more equitable healthcare system.
| Resource | Impact on Health Disparities |
|---|---|
| Health Education | Increases health literacy and empowers communities |
| Healthcare Facilities | Improves access to medical services |
| Community Health Programs | Addresses specific health needs and promotes prevention |
Legislative Changes
Legislative changes are essential for addressing health disparities. Laws and regulations can create a framework for equitable healthcare. These changes can address systemic inequality and improve health outcomes for marginalized communities.
Some key legislative changes to consider include:
- Universal Healthcare: Ensuring that everyone has access to healthcare regardless of socioeconomic status.
- Anti-Discrimination Laws: Preventing discrimination in healthcare settings.
- Funding for Public Health Policy: Supporting initiatives that address health disparities and promote equity in healthcare.
Legislative changes can also address social determinants of health. For example, policies that promote affordable housing and education can improve community health. By addressing these underlying factors, policymakers can create a more equitable society.
| Legislation | Impact on Health Disparities |
|---|---|
| Universal Healthcare | Ensures access to healthcare for all |
| Anti-Discrimination Laws | Prevents discrimination and promotes equity |
| Funding for Public Health Policy | Supports initiatives to address health disparities |
In summary, understanding the reasons underlying health inequalities is crucial for effective policy-making. By focusing on resource allocation and legislative changes, policymakers can address health disparities and promote equity in healthcare.
Role Of Education
Understanding the reasons behind health inequalities is crucial to fostering a healthier society. Education plays a significant role in addressing these disparities. It empowers individuals with the knowledge needed to make informed health decisions. This, in turn, promotes health equity and reduces health outcome disparities. Let’s delve into two key aspects: Awareness Programs and Access to Information.
Awareness Programs
Awareness programs are essential tools in promoting health equity. They provide education on various health topics, ensuring that communities understand preventive health measures and healthy lifestyle choices. These programs aim to reduce health disparities by addressing the social determinants of health and emphasizing cultural competency.
Effective awareness programs often include:
- Workshops on nutrition and exercise
- Seminars on disease prevention
- Community health fairs
- Educational campaigns on mental health
These initiatives can be particularly impactful in underserved communities where health information may be scarce. By offering accessible health education, awareness programs can bridge the gap in healthcare access and improve overall health outcomes.
| Program Type | Target Audience | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrition Workshops | Low-income families | Improved dietary habits |
| Disease Prevention Seminars | Adults | Reduced incidence of chronic diseases |
| Mental Health Campaigns | Youth | Increased awareness and support |
By educating the public, these programs help communities make healthier choices, ultimately leading to more equitable healthcare access.
Access To Information
Access to accurate and timely health information is a cornerstone of equitable healthcare access. Knowledge empowers individuals to take preventive health measures and seek timely medical care. This reduces health outcome disparities across different socioeconomic groups.
Key ways to improve access to information include:
- Developing user-friendly health portals
- Providing multilingual resources
- Offering free online health courses
- Distributing printed materials in community centers
Health portals should be easy to navigate and provide comprehensive information on various health topics. These platforms should also consider cultural competency to cater to diverse populations. For instance, offering resources in multiple languages ensures that non-English speakers receive the necessary information.
Here’s a simple approach to improve access to information:
- Create a centralized online health portal.
- Ensure content is available in multiple languages.
- Regularly update the portal with the latest health guidelines.
- Promote the portal through community health education programs.
Educational materials distributed at community centers can also make a significant impact. These materials should cover topics such as preventive health measures and the importance of regular check-ups. By making health information more accessible, communities can make informed decisions, leading to better health outcomes and reduced health disparities.
Cultural Influences
Understanding the reasons underlying health inequalities is crucial for improving public health. Cultural influences play a significant role in shaping health behaviors and outcomes. These influences can create disparities in access to healthcare and affect the effectiveness of health interventions. By examining cultural factors, we can develop more inclusive public health policies and promote equity in healthcare.
Beliefs And Practices
Cultural beliefs and practices significantly impact health behaviors and healthcare utilization. Different cultures have unique views on health, illness, and treatment, which can lead to varied health outcomes. Here are some key aspects:
- Traditional Medicine: Many communities rely on traditional medicine and healers. This can delay seeking modern medical treatment.
- Religious Practices: Religious beliefs may influence decisions about medical procedures, such as blood transfusions or vaccinations.
- Dietary Habits: Cultural dietary practices can affect nutritional status and risk of chronic diseases.
Consider the following table, which outlines how cultural beliefs impact health:
| Cultural Belief | Impact on Health |
|---|---|
| Use of Herbal Remedies | May interact with prescribed medications |
| Fasting during Religious Observances | Can affect chronic disease management |
| Stigma around Mental Health | Leads to underutilization of mental health services |
Addressing these cultural beliefs and practices requires cultural competence. Healthcare providers need to understand and respect different cultural backgrounds to improve health literacy and promote better health outcomes.
Language Barriers
Language barriers are a significant obstacle to accessing healthcare. They can hinder communication between patients and healthcare providers, leading to misdiagnoses and poor health outcomes. Here are some challenges posed by language barriers:
- Misunderstanding Medical Instructions: Patients may not understand how to take medications or follow treatment plans.
- Limited Health Literacy: Non-native speakers may struggle to comprehend health information and services.
- Reduced Patient Engagement: Language barriers can prevent patients from asking questions or expressing concerns.
To mitigate these issues, healthcare systems should implement the following strategies:
- Provide professional medical interpreters to facilitate communication.
- Offer health materials in multiple languages to improve health literacy.
- Train healthcare providers in cultural competence to better understand diverse patient needs.
Addressing language barriers is essential for promoting equity in healthcare. It ensures that all patients receive the care they need, regardless of their language proficiency. By prioritizing these efforts, we can reduce health disparities and improve community health initiatives.
Health Systems And Access
Understanding the reasons behind health inequalities is crucial. Different factors influence health disparities, and access to healthcare is a major one. A well-functioning health system ensures everyone can get the care they need. Accessibility impacts health outcomes, preventive care, and overall public health. Let’s explore two critical aspects: insurance coverage and the availability of services.
Insurance Coverage
Insurance coverage plays a significant role in healthcare accessibility. People with health insurance are more likely to get preventive care and necessary treatments. Those without insurance face many barriers, impacting their health outcomes.
Key Points:
- Health Disparities: Lack of insurance creates gaps in care, leading to health disparities.
- Systemic Barriers: High costs and complex systems prevent many from getting coverage.
- Socioeconomic Status: Low-income individuals often cannot afford insurance, affecting their access to healthcare.
Here’s a table showing the impact of insurance coverage on health outcomes:
| Insurance Status | Access To Preventive Care | Health Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Insured | High | Better |
| Uninsured | Low | Poor |
Insurance coverage directly affects equity in healthcare. Ensuring everyone has access to affordable insurance can reduce health disparities and improve public health.
Availability Of Services
The availability of healthcare services is another critical factor. Even with insurance, people need access to providers and facilities. Rural and underserved areas often lack these services, creating systemic barriers.
Key Points:
- Healthcare Accessibility: Availability of services determines how easily people can get care.
- Social Determinants Of Health: Factors like location and socioeconomic status influence service availability.
- Health Outcomes: Limited services lead to delayed care and worse health outcomes.
Consider the following data on service availability:
| Area Type | Number of Providers | Average Wait Time |
|---|---|---|
| Urban | High | Short |
| Rural | Low | Long |
Equity in healthcare means ensuring services are available to all, regardless of location or socioeconomic status. Improving service availability can enhance health outcomes and reduce health disparities.
Long-term Economic Effects
Understanding the reasons underlying health inequalities is important for many reasons. One significant aspect is the long-term economic effects. These effects are often overlooked but are crucial to consider. Health inequalities don’t just impact individuals; they have a wider economic impact. This includes reduced workforce productivity and increased healthcare costs. Addressing these issues can lead to better public health outcomes and a more robust economy.
Workforce Productivity
Health inequalities directly affect workforce productivity. When people lack access to healthcare, they are more likely to suffer from chronic illnesses. This leads to increased absenteeism and lower work performance. Healthy workers are productive workers. Therefore, achieving health equity can boost economic growth.
Consider these points:
- Chronic Illness: Employees with chronic health issues miss more workdays. This reduces overall productivity.
- Mental Health: Poor mental health impacts focus and efficiency at work.
- Workplace Injuries: Lack of preventative healthcare leads to more workplace injuries.
A study shows that improving health disparities can increase GDP by 1-2%. This is because healthier employees contribute more effectively to the economy.
| Health Factor | Impact on Productivity |
|---|---|
| Chronic Illness | Higher absenteeism and reduced efficiency |
| Mental Health Issues | Lower focus and productivity |
| Workplace Injuries | Increased days off work |
Addressing social determinants of health like education and income can improve workforce productivity. Better health leads to fewer sick days and higher efficiency. This ultimately benefits the economy as a whole.
Healthcare Costs
Health inequalities also lead to higher healthcare costs. People who lack access to healthcare often rely on emergency services. This is more expensive than preventative healthcare. Preventative healthcare is crucial for reducing long-term healthcare costs.
Here are some examples:
- Emergency Room Visits: Cost more than regular doctor visits.
- Hospital Admissions: Chronic illnesses lead to frequent hospital stays.
- Medications: Lack of preventative care leads to expensive treatments.
A report shows that the economic impact of health inequalities costs the U.S. billions each year. By focusing on health equity, we can reduce these costs. This involves addressing socioeconomic factors and providing better access to healthcare.
| Healthcare Service | Cost Comparison |
|---|---|
| Emergency Room Visit | $1,000 – $2,000 |
| Regular Doctor Visit | $100 – $200 |
| Hospital Admission | $10,000 – $20,000 |
Implementing preventative healthcare can save money in the long run. This also leads to better public health outcomes. Equity in healthcare is not just a moral issue; it makes economic sense. Improving population health reduces the overall burden on the healthcare system. This allows resources to be used more efficiently.

Credit: twitter.com
Strategies For Change
Understanding the reasons behind health inequalities is crucial for creating effective strategies for change. These strategies can bridge gaps in access to healthcare, address health disparities, and promote equity in healthcare. By focusing on community initiatives and collaboration with stakeholders, we can create targeted solutions that improve health outcomes for all.
Community Initiatives
Community initiatives play a vital role in addressing health disparities. Local programs can directly target the specific needs of a community, providing access to healthcare and health education. These initiatives often include:
- Health Education Workshops: Teaching community members about nutrition, exercise, and preventive care.
- Mobile Health Clinics: Bringing healthcare services to underserved areas.
- Community Health Programs: Offering free or low-cost screenings, vaccinations, and treatments.
These programs increase awareness and provide essential services to those who might not otherwise have access. For instance, mobile health clinics can reach remote or socioeconomically disadvantaged areas, ensuring equitable healthcare access.
Furthermore, community initiatives can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility among residents. By involving local leaders and members in planning and execution, these programs can be more culturally competent and effective. This engagement also helps in identifying and addressing social determinants of health specific to the community.
Key Benefits of Community Initiatives:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Access | Providing healthcare services where they are needed most. |
| Improved Health Education | Educating communities on health and wellness. |
| Cultural Competence | Ensuring programs respect and understand local cultures. |
Collaboration With Stakeholders
Collaboration with stakeholders is essential for sustainable change. Engaging various stakeholders, such as government agencies, non-profits, and private sector partners, can amplify efforts to reduce health disparities.
Key Stakeholders:
- Government Agencies: Responsible for public health policies and funding.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Provide community health programs and advocacy.
- Private Sector: Can offer resources and innovative solutions.
Effective stakeholder engagement can drive policy changes that address socioeconomic factors and social determinants of health. For instance, collaboration with government agencies can lead to better funding for community health programs. Partnerships with non-profits can bring in expertise and resources for targeted interventions.
Businesses can also contribute by investing in community health initiatives and promoting workplace wellness programs. This multi-sector approach ensures a comprehensive strategy that tackles health inequities from various angles.
Examples of Successful Collaboration:
| Project | Stakeholders Involved | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy Cities Initiative | Local Government, Non-Profits, Businesses | Improved access to parks and recreational facilities. |
| Community Health Workers Program | Healthcare Providers, Community Organizations | Increased health education and screenings. |
| Workplace Wellness Programs | Corporations, Health Insurers | Reduced healthcare costs and improved employee health. |
Collaborative efforts create a synergistic effect, making it easier to address complex health challenges. By working together, stakeholders can share knowledge, resources, and strategies to create a healthier society for all.

Credit: mtha.org
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes Health Inequalities?
Health inequalities stem from various social, economic, and environmental factors. These include income, education, housing, and access to healthcare. Understanding these determinants is crucial.
How Do Health Inequalities Affect Society?
Health inequalities lead to disparities in health outcomes. This affects individuals and burdens healthcare systems. Addressing these issues can improve overall societal well-being.
Why Study Health Inequalities?
Studying health inequalities helps identify and address root causes. This can lead to better health policies and improved public health outcomes.
Can Health Inequalities Be Reduced?
Yes, health inequalities can be reduced through targeted interventions. Policies focusing on education, income, and healthcare access can make a significant difference.
Conclusion
Understanding health inequalities is crucial for a healthier society. It helps identify areas needing attention. By addressing these issues, we can improve overall health. Everyone deserves equal access to healthcare. Awareness leads to better policies and fairer systems. Healthier communities benefit us all.
Knowledge empowers action. Let’s work together to reduce health disparities. A brighter, healthier future awaits.

“As the voice behind Radiant Glow Health, we are dedicated to being your ultimate wellness and vitality companion. Our mission is to inspire and guide you on your journey to a healthier and more vibrant life. Join us as we explore holistic health practices and empower you to radiate wellness from within.”



